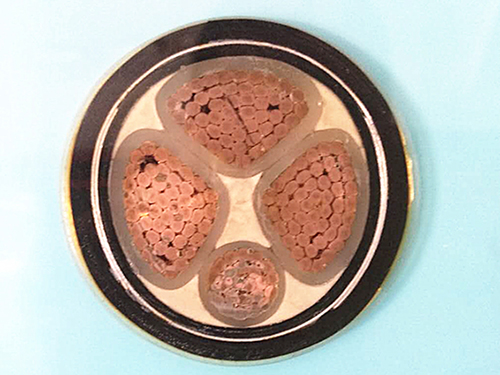
Low smoke halogen-free cross-linked power cable WDZ-YJY23-0.6
Low smoke zero halogen cross-linked power cable WDZ-YJY23-0.6 (Low smoke zero halogen), abbreviated as LSZH, LSOH, LS0H, LSFH, and OHLS, is a material classification for wire sheaths in the wire and cable industry. The low smoke halogen-free wire sheath is composed of thermoplastic or thermosetting materials that have low smoke exhaust when heated and do not contain halogens themselves.
Most network cable coatings are composed of polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride, or thermoplastic polyurethane. If caught on fire, chlorine containing plastics will release toxic hydrogen chloride, and if they come into contact with water, they will produce hydrochloric acid. Low smoke halogen-free materials do not release hydrogen halides or other acids when ignited.
Low smoke halogen-free materials can reduce the toxic and corrosive gases generated during their combustion. Low smoke and halogen-free materials are often used in poorly ventilated environments such as airplanes, train carriages, or ships. Low smoke and halogen-free materials are also commonly used in the railway industry, as there are high-voltage lines or signal lines underneath the railway that transmit train positions. The use of low smoke and halogen-free materials also reduces the accumulation of toxic gases in the event of fire or short circuit damage to the circuit.
In industries such as railways or shipbuilding, an important requirement is to protect personnel and equipment from exposure to toxic and corrosive gases. In these situations, it is required to use low smoke and halogen-free materials on the outer layer of wires and cables.
A cable is a single component formed by bonding, twisting, or weaving two or more wires together to connect two devices and transmit electrical signals. Cables have a wide range of applications and are needed for every purpose, ranging from transmitting electrical energy and signals to wire products that convert electromagnetic energy.
Power cables are usually composed of cable cores that transmit electricity or electrical signals, and protective and insulating sheaths. A cable with only one core and a thinner diameter is usually called a wire. Some wires do not have insulation sheaths and are called bare wires. The cable core in the cable is made of a metal material with good conductivity, usually copper (with good conductivity) or aluminum (with lower cost).